8 Factors to Assess the Costs of Software Development
July 25th, 2024

Software development costs can vary widely depending on several factors. Whether you’re a startup looking to create a new app or a large enterprise implementing a complex system, understanding these factors can help you budget effectively and make informed decisions. In this detailed blog post, we’ll delve into the key elements that influence software development costs, supported by data and insights from various sources.
1
Determining the Complexity Of Your Project
The complexity of your software project is one of the most significant factors influencing cost. Complexity can be broken down into 2 components:
-
Scope of Features: A project with a simple set of features will cost less than one with numerous, intricate functionalities. For instance, a basic mobile app might include user login, profile management, and a few core features, while a complex enterprise application might integrate with multiple systems, handle large data volumes, and provide advanced analytics.
-
Custom Requirements: Custom software tailored to specific business needs typically incurs higher costs. This is because custom development requires more design, coding, and testing to ensure that the software meets unique requirements.
According to a survey by GoodFirms, the cost of developing a simple app ranges from $38,000 to $91,000, while more complex apps can cost anywhere from $55,550 to $131,000. These figures highlight how significantly complexity can impact development costs.
2
Development Team Qualities
The size and expertise of your development team also play a crucial role in determining the cost:
-
Team Size: Larger teams can deliver projects faster but at a higher cost. Smaller teams might be more cost-effective but could take longer to complete the project. Balancing team size with project timelines is essential to manage costs effectively.
-
Expertise: Specialized skills often come with a premium. Hiring experienced developers with niche expertise might increase costs but can lead to higher quality outcomes and faster problem-solving.
-
In-House vs. Outsourcing: Hiring an in-house team can be expensive due to salaries, benefits, and overhead costs. Outsourcing to a development agency or freelance developers can be more economical, especially if the project requires specific skills. Clutch reports that the average hourly rate for a software developer for apps can range from $25 to $49 depending on their location and expertise.
3
Technology Stack
The choice of technology stack—comprising the programming languages, frameworks, and tools used—can significantly affect both the development cost and the future scalability and maintenance of the software.
Open Source vs. Proprietary Tools
Open-source tools can reduce initial costs, but proprietary tools might offer better support and additional features that justify their cost. For example, using an open-source database like MySQL is free, while a proprietary database like Microsoft SQL Server requires licensing fees.
Modern vs. Legacy Technologies
Developing with modern technologies can be more efficient and cost-effective in the long run. Legacy technologies might seem cheaper initially but can lead to higher maintenance costs and limited scalability. For instance, building a web application using the latest version of React or NextJS can be more cost-efficient over time compared to using an outdated framework.
4
Your Development Timeline
The development timeline is directly proportional to cost. Projects with tight deadlines often require more resources and overtime, increasing costs.
For example, Agile development allows for iterative progress with continuous feedback and adjustments, which can help manage costs better. However, it may still result in higher costs if the project scope is not well-defined from the outset. The Waterfall model, being more linear, can be less flexible and may lead to higher costs if changes are needed late in the process. Agile projects are also 28% more successful than traditional Waterfall projects, suggesting that Agile might offer better cost management through its iterative approach.
5
Design and User Experience (UX)
Investing in a good design and user experience (UX) is crucial for the success of any software product. High-quality design and UX services can be costly but offer significant long-term benefits.
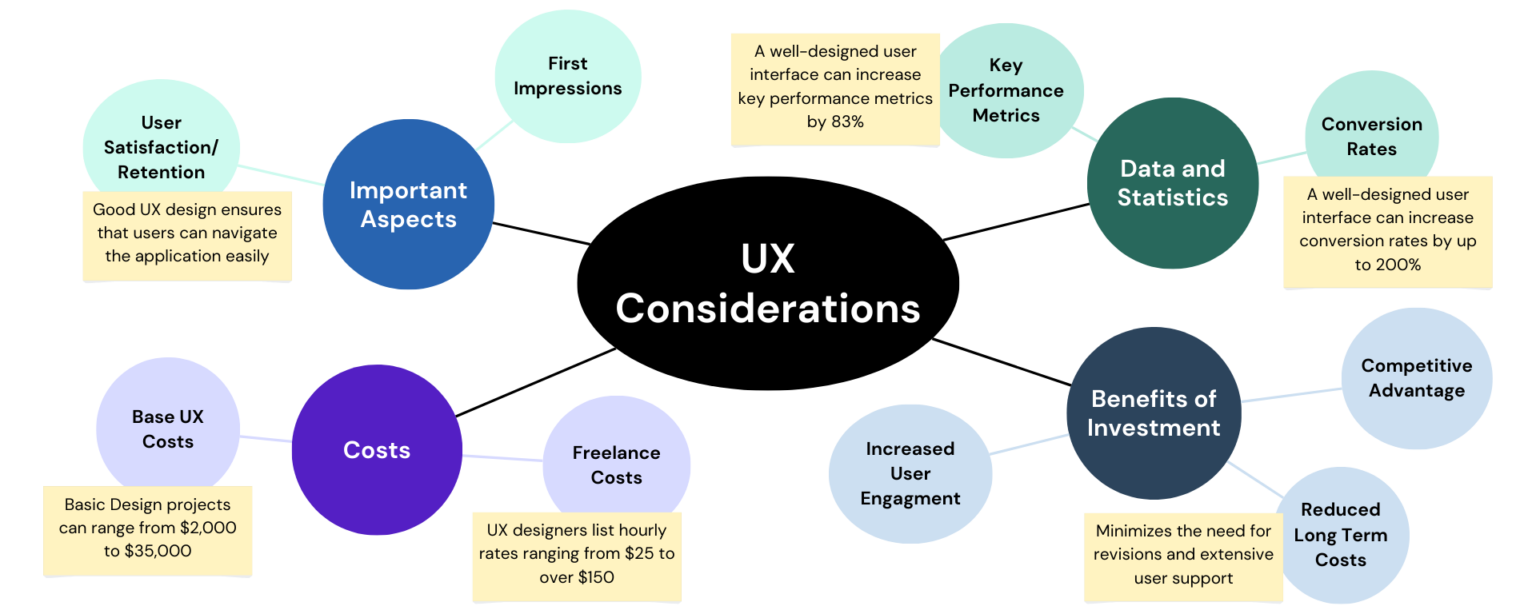
A well-designed product not only attracts users but also reduces the need for extensive user training and support, thus saving costs in the long run.
6
Testing and Quality Assurance
Rigorous testing and quality assurance (QA) are essential to ensure the software works as intended and is free of bugs. This phase is crucial because it verifies that the software performs correctly under various conditions, meets the specified requirements, and provides a seamless user experience. Testing and QA can account for a significant portion of the development cost due to the extensive efforts required.
One important aspect of QA is the distinction between automated and manual testing. Automated testing can be more cost-effective in the long run, especially for large projects with repetitive tasks. It involves writing scripts and using tools to automatically run tests, which can quickly identify issues in the software. However, automated testing requires an initial investment to set up the testing infrastructure and develop the test scripts. This setup phase can be time-consuming and requires skilled professionals who can write and maintain the automation scripts.
On the other hand, manual testing is indispensable for usability testing and finding issues that automated tests might miss. It involves human testers interacting with the software as end-users would, ensuring that the software is intuitive and user-friendly. Manual testers can provide valuable feedback on the overall user experience and detect subtle bugs or usability issues that automated tests may overlook. Despite being labor-intensive and potentially more expensive in terms of labor costs, manual testing remains a critical component of a comprehensive QA strategy.
Graphic from TechnoLush
According to TestFort, the cost of QA and testing can range from 15% to 25% of the total development budget. This includes the expenses for setting up test environments, writing test cases, and performing both manual and automated tests. The actual percentage can vary depending on the project’s complexity, the testing methods employed, and the quality standards required. For example, a highly regulated industry such as healthcare or finance may demand more rigorous testing protocols, thereby increasing the overall QA costs.
7
Post-Development Costs
The costs don’t end with the completion of development. Ongoing maintenance, updates, and support are necessary to keep the software running smoothly and securely:
-
Maintenance and Updates: Regular updates to fix bugs, add new features, and ensure compatibility with new technologies can be a recurring cost. According to DZone, maintenance costs can be about 15-20% of the original development cost annually.
-
Hosting and Infrastructure: For web and mobile applications, hosting costs can vary widely based on the expected user base and data storage requirements. Cloud services like AWS, Azure, and Google Cloud offer scalable solutions that can help manage these costs effectively.
8
Choosing Your Team
The geographical location of your development team can significantly impact costs. Developers in North America and Western Europe typically charge higher rates than those in Eastern Europe, Asia, or Latin America:
- Offshoring and Nearshoring: Offshoring to countries with lower labor costs can reduce development expenses. Nearshoring, working with teams in nearby countries with similar time zones, can balance cost savings with easier communication and collaboration.
A report by Accelerance highlights that hourly rates for developers can be as low as $25 in countries like India or Ukraine, compared to $100-$150 in the United States or Western Europe.
Real World Examples
Examining Costs of Software Development: Examples

Initially developed by a small team, Instagram’s development cost was relatively low. The app’s simple yet powerful features focused on photo sharing, which allowed for a lean development process.

AirBnb
The development of Airbnb involved complex features like user profiles, listings, payments, and a robust search engine. The project required a larger team and more resources, leading to higher development costs.
Conclusion
Interested in building a new solution?
Understanding the cost of software development requires considering multiple factors, from project complexity and team size to technology stack and post-development costs. By carefully planning and managing these elements, businesses can optimize their software development investments and achieve successful outcomes.
Contact DevDefy if you’re looking to find out pricing and software development strategy within your company!


